soil food webs are fueled by which of the following
Soil food web soil health 32 all food webs are fueled. All food webs are fueled by the primary producers.
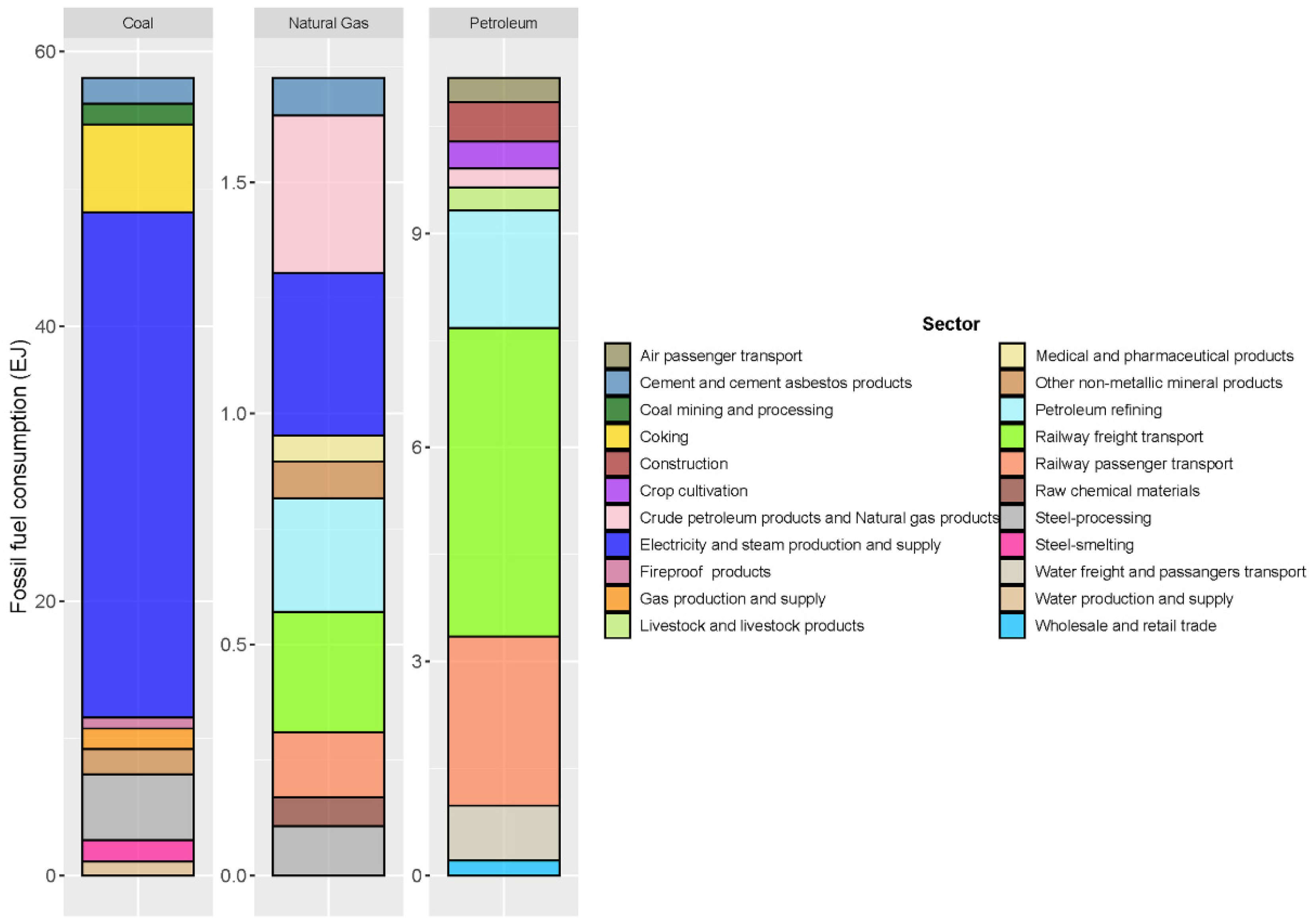
Sustainability Free Full Text The Coal Petroleum And Gas Embedded In The Sectoral Demand And Supply Chain Evidence From China Html
A food web diagram shows a series of conversions represented by arrows of energy and nutrients as one organism eats another see food web diagram below.

. Two main food web pathways are presumed to account for carbon fluxes through most soil food webs. Causes erosion replaces soil lost to erosion leaches nutrients out of the soil is bad for the soil. Across all four countries soil food web structure was strongly influenced by land use SI Appendix Tables S1 and S2The number of feeding groups total biomass of the soil food web and biomass of the fungal bacterial and root energy channel which consists of arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi AMF root-feeding fauna and their predators.
This is all fueled by the microorganisms breaking it down. Display the following graphics and video clips and then. The following chart shows that.
Which of the following is NOT mentioned as a reason for a fertile soil not being productive soil. These differences are the result of soil vegetation and climate factors as well as land management practices. Course Title AA 1.
Students who viewed this also studied. The soil food web naturally supports plant health and protects plants from attack. Soil Biology Primer The phospholipid fatty acid PLFA test can be used to measure the activity of the soil food web.
Photosynthesis results in plants using the suns energy to fix carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. All food webs are fueled by the primary producers. The producers in soil food webs include.
The plants lichens moss photosynthetic bacteria and algae that use the suns energy to fix carbon dioxide. Soil food webs are fueled by which of the following. This is the first trophic level.
The soil food web refers to the complex relationships between the diverse groups of fauna and flora found in soil. The soil food web is the community of organisms living all or part of their lives in the soil. Teachers may use these materials to develop lectures student reading materials or as resources for further investigations.
Pages 3 This preview shows page 3 out of 3 pages. Soil Ecology Day 1. Soil nematodes are ubiquitous inhabitants of soil ecosystems and occupy a central position in soil micro food webs Pen-Mouratov et al 2003 Yeates 2003.
Within all soil food webs sfw there is a perceived paradox between the large diversity of organisms densely packed within space and time and the level of feeding specialization. Soil productivity describes the performance of a soil based on all BUT which of the following attributes. The composition of each specific web is greatly influenced by biological chemical and physical forces in the environment.
Breaking with the dogma that sfws are fueled by plant that within this food web. The Channel Index CI is calculated as the proportion of fungal-feeding nematodes compared to enrichment-opportunistic bacterial feeders and is an indicator of activity in the predominant decomposition channels in the soil fungal mediated higher values or. These groups include bacteria fungi protozoa nematodes microarthropods and the larger plants and animals found in and around soil.
Omnivores - ants earthworms and dorylaimi nematodes Carnivores - tiger beetle predatory mites and centipedes. Herbivores - wireworms milkweed beetles and white potato cyst nematodes. The soil food web begins with the energy from the sun which triggers photosynthesis in plants.
Take time to review the questions and conclusions from the labs. The dynamics of soil food webs play a key role in determining the ecological response of terrestrial ecosystems to current and future environmental change. Elevated CO 2 warming and altered precipitation during global change Blankinship et al 2011 and may also be influenced indirectly due to the variation in the inputs of root and leaf litter.
The soil food web is the community of organisms living all or part of their lives in the soil. Results and Discussion. Use Know Soil Know Life Table 3-2 to build an understanding of soil fauna.
Both root and leaf litter fuel the micro-food webs microorganisms and nematodes in. All food webs are fueled by the primary producers. View Maria Parsley - Soil Day 1 from BIO MISC at Sioux Falls Christian Schools.
One of the main causes according to the UN is intensive agriculture and specifically pesticides. Soil Food Web Go to the following NRCS link and. Desoto Central High School.
Organisms and their interaction the soil food web is the community of organisms living all or part of their lives in the soil. A beetles B centipedes C earthworms D scorpions Decomposition of organic matter in the soil. These organisms live all or part of their life cycle in the soil and are respon-sible for converting energy as one organism consumes another.
-All food webs are fueled by the primary producers. Each field forest or pasture has a unique soil food web with a particular proportion of bacteria fungi and other groups and a particular level of complexity within each group of organisms. They are also good indicators for evaluating soil food web structure and function Neher 2001 Wasilewska 2006.
With the soil food web in place and the use of natural farming practices pesticides are not required. This process creates the carbon and organic compounds contained in plant material. The quality of the C generally differs substantially between root and leaf litters Ma et al 2016 and soil food webs are influenced directly by the environmental changes eg.
Make up the soil food web. The plants lichens moss photosynthetic bacteria and algae that use the. The plants lichens moss photosynthetic bacteria and algae that use the suns energy to fix carbon dioxide from the atmosphere-Most other soil organisms get energy and carbon by consuming the organic compounds found in plants other organisms and waste by-products-A few bacteria called chemoautotrophs get.
Parent material which develops from rock fragments which fall from greater heights due to gravity. Trophic level nematodes and indicates soil food web length and soil resilience. A roots B lichens C photosynthetic bacteria D algae E all of the above All of the following are soil arthropods EXCEPT.

Earth Day Composting Life Cycle Clipart Conservation Glitter Meets Glue In 2022 Life Cycles Cycle For Kids Compost
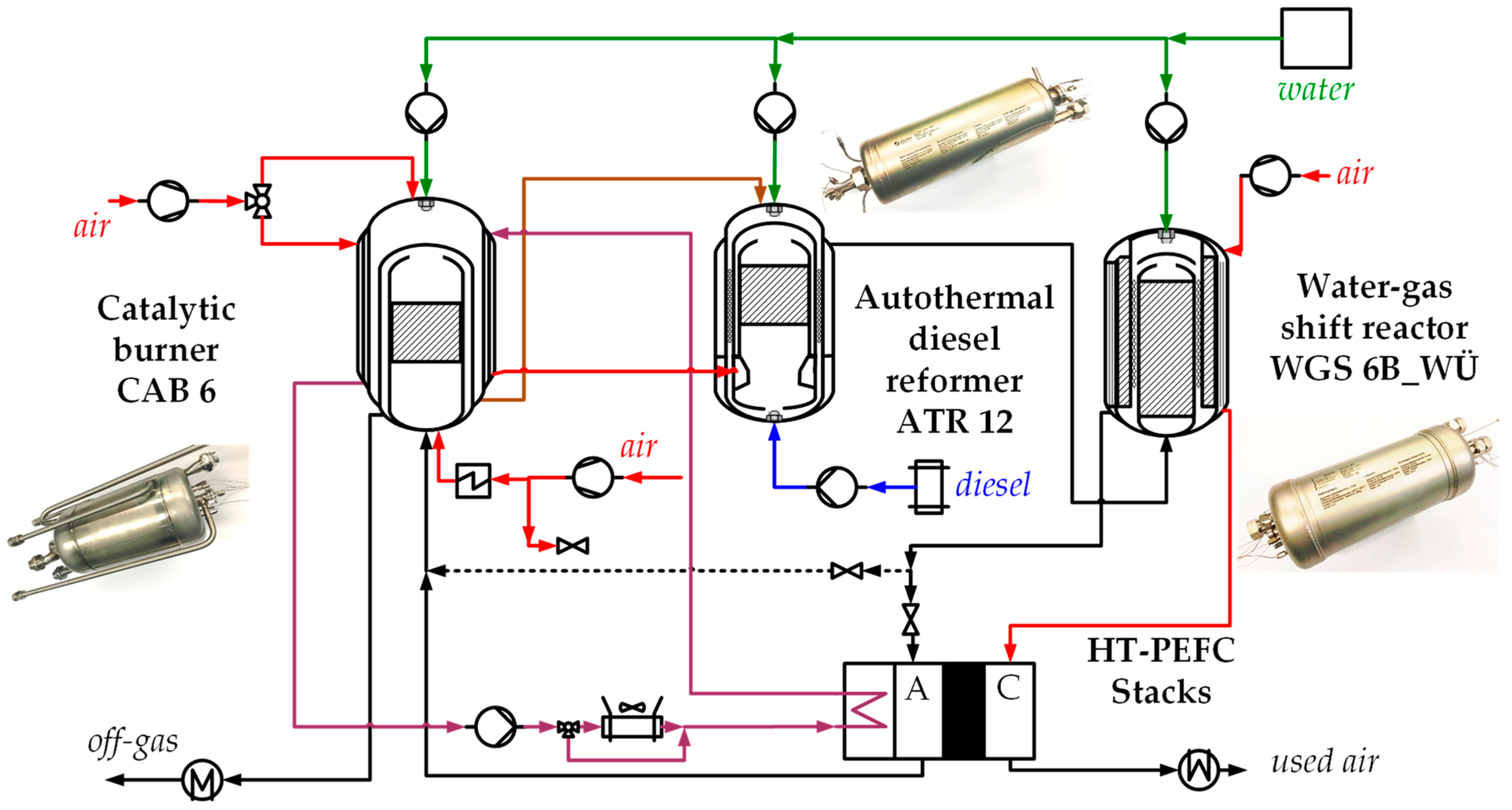
Energies Free Full Text A Compact Self Sustaining Fuel Cell Auxiliary Power Unit Operated On Diesel Fuel Html

Orca Fuel Solutions Home Facebook
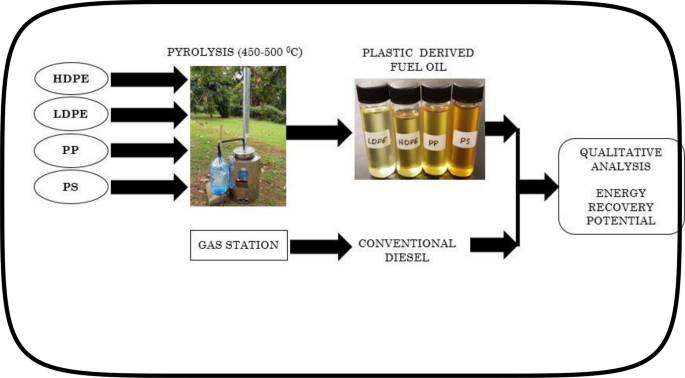
Qualitative And Energy Recovery Potential Analysis Plastic Derived Fuel Oil Versus Conventional Diesel Oil Springerlink

Celebrating 100 Years Of Industrial Nitrogen Fixation Ian Ecocheck Blog Nitrogen Cycle Nitrogen Fixation Nitrogen

Maintaining Healthy Hydro Roots To Avoid Root Rot In 2021 Plant Health Hydro Plant Hydroponic Growing

Data Visualisation Infographic Pinterest Data Visualization Map Infographic Map Data Visualization Design
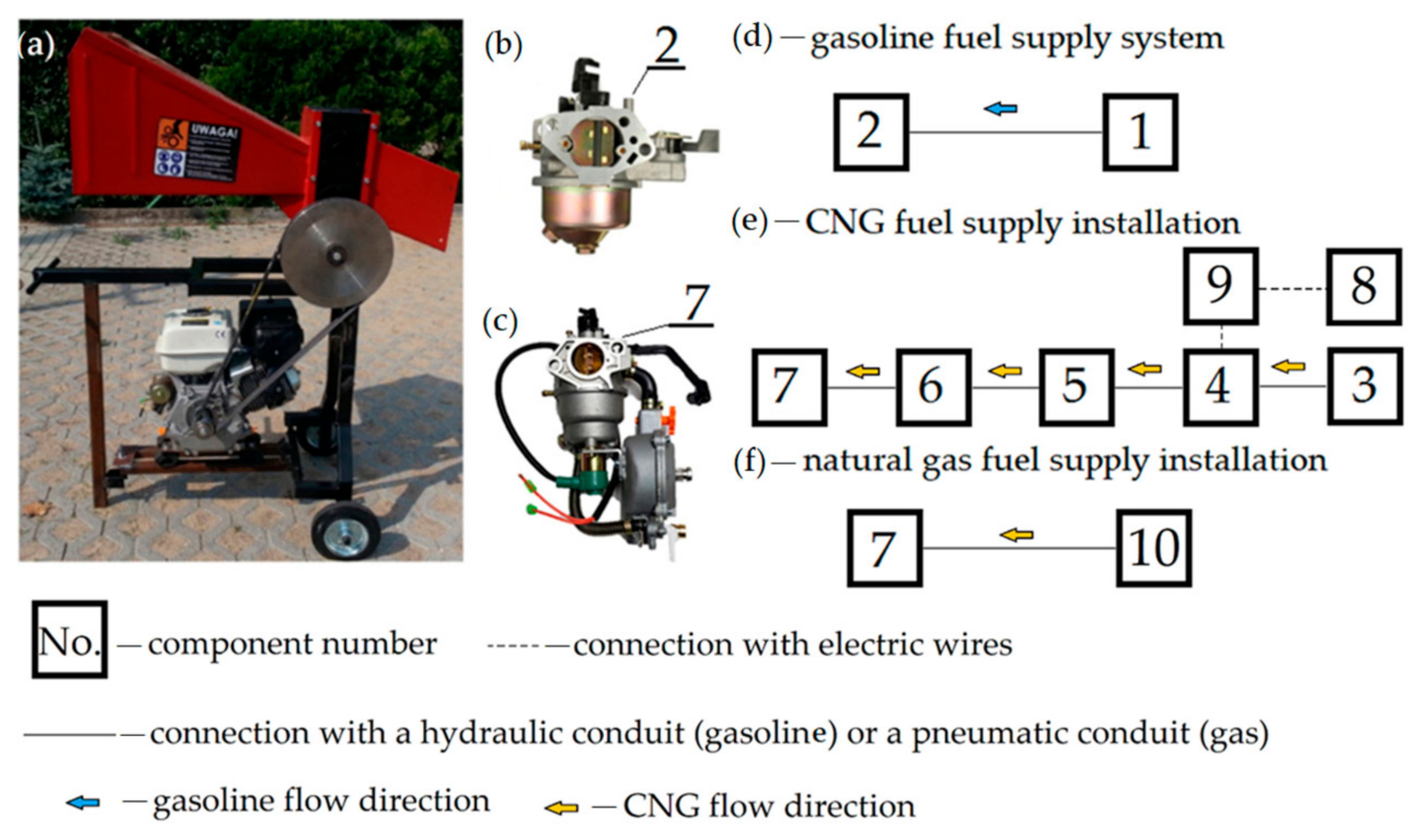
Energies Free Full Text Impact Of Compressed Natural Gas Cng Fuel Systems In Small Engine Wood Chippers On Exhaust Emissions And Fuel Consumption Html

Austin Texas Plans 2 Acre Food Forest City Farmer News Food Forest Permaculture Design Urban Forestry

Algae Fuel Process Aquaponics System Aquaponics Greenhouse Gases
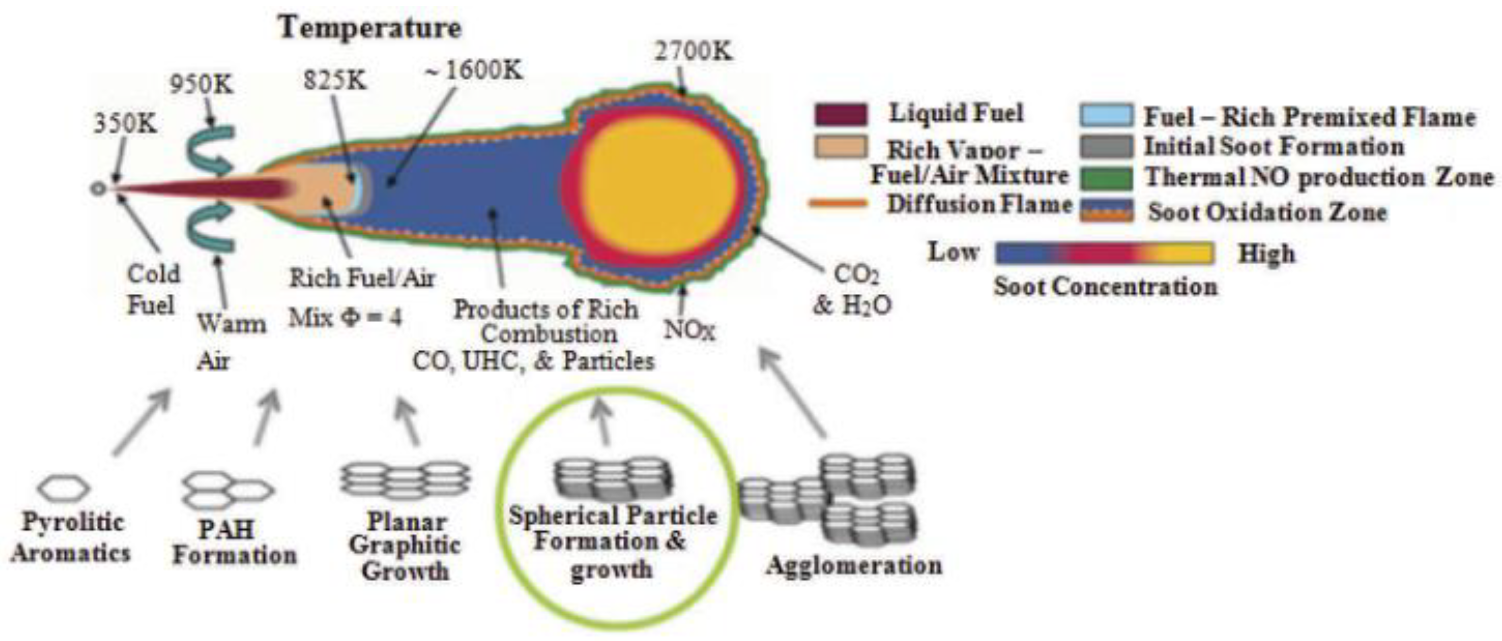
Catalysts Free Full Text The Impact Of Alternative Fuels On Ship Engine Emissions And Aftertreatment Systems A Review Html

Vegetable And Flowers Mingle In Borders Together Vegetable Crops Can Be Set In And Around Flower Borders To C Container Plants Vegetable Garden Planning Plants

A Direct Carbon Solid Oxide Fuel Cell Fueled With Char From Wheat Straw Cai 2019 International Journal Of Energy Research Wiley Online Library

Amazon Rainforest Plants Banana Google Search Banana Fruit Banana Tree




